前言
上篇我们介绍了Spring Boot对传统JdbcTemplate的集成,这次换一下,介绍下Spring Boot中如何集成MyBatis。这里分别介绍注解方式以及XML方式的整合。喜欢哪种方式自己选择。
正文
项目框架还是跟上一篇一样使用Spring Boot的ace后端模板,你可以基于它来跟着博主一起来调整代码,如果没看过上一篇,那就下载本篇源码研究吧。
跟上篇一样先添加基础的依赖和数据源。
添加依赖
这里需要添加mybatis-spring-boot-starter依赖跟mysql依赖1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11<!--最新版本,匹配spring Boot1.5 or higher-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.mybatis.spring.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>mybatis-spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
<version>1.3.0</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
</dependency>
这里不引入spring-boot-starter-jdbc依赖,是由于mybatis-spring-boot-starter中已经包含了此依赖。
博主开始整理的时候发现mybatis-spring-boot-starter有新版本了,这里就集成最新的,匹配Spring Boot1.5版本。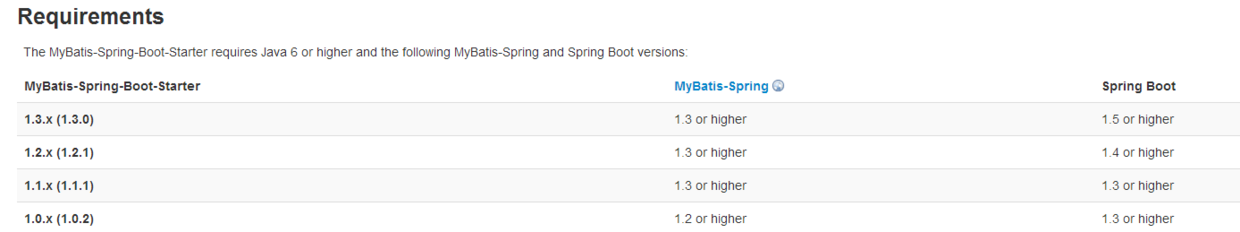
MyBatis-Spring-Boot-Starter依赖将会提供如下:
- 自动检测现有的DataSource
- 将创建并注册SqlSessionFactory的实例,该实例使用SqlSessionFactoryBean将该DataSource作为输入进行传递
- 将创建并注册从SqlSessionFactory中获取的SqlSessionTemplate的实例。
- 自动扫描您的mappers,将它们链接到SqlSessionTemplate并将其注册到Spring上下文,以便将它们注入到您的bean中。
就是说,使用了该Starter之后,只需要定义一个DataSource即可(application.properties中可配置),它会自动创建使用该DataSource的SqlSessionFactoryBean以及SqlSessionTemplate。会自动扫描你的Mappers,连接到SqlSessionTemplate,并注册到Spring上下文中。
数据源配置
在src/main/resources/application.properties中配置数据源信息。
1 | spring.datasource.url = jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/spring?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf-8 |
自定义数据源
Spring Boot默认使用tomcat-jdbc数据源,如果你想使用其他的数据源,比如这里使用了阿里巴巴的数据池管理,除了在application.properties配置数据源之外,你应该额外添加以下依赖:1
2
3
4
5<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba</groupId>
<artifactId>druid</artifactId>
<version>1.0.19</version>
</dependency>
修改Application.java1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
public class Application {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(Application.class, args);
}
private Environment env;
//destroy-method="close"的作用是当数据库连接不使用的时候,就把该连接重新放到数据池中,方便下次使用调用.
(destroyMethod = "close")
public DataSource dataSource() {
DruidDataSource dataSource = new DruidDataSource();
dataSource.setUrl(env.getProperty("spring.datasource.url"));
dataSource.setUsername(env.getProperty("spring.datasource.username"));//用户名
dataSource.setPassword(env.getProperty("spring.datasource.password"));//密码
dataSource.setDriverClassName(env.getProperty("spring.datasource.driver-class-name"));
dataSource.setInitialSize(2);//初始化时建立物理连接的个数
dataSource.setMaxActive(20);//最大连接池数量
dataSource.setMinIdle(0);//最小连接池数量
dataSource.setMaxWait(60000);//获取连接时最大等待时间,单位毫秒。
dataSource.setValidationQuery("SELECT 1");//用来检测连接是否有效的sql
dataSource.setTestOnBorrow(false);//申请连接时执行validationQuery检测连接是否有效
dataSource.setTestWhileIdle(true);//建议配置为true,不影响性能,并且保证安全性。
dataSource.setPoolPreparedStatements(false);//是否缓存preparedStatement,也就是PSCache
return dataSource;
}
}
ok这样就算自己配置了一个DataSource,Spring Boot会智能地选择我们自己配置的这个DataSource实例。
脚本初始化
1 | CREATE DATABASE /*!32312 IF NOT EXISTS*/`spring` /*!40100 DEFAULT CHARACTER SET utf8 */; |
注解方式跟XML配置方式共同的模块编码
不管是注解方式还是XML配置的方式,以下代码模块都是一样的
实体对象
1 | public class LearnResouce { |
Controller层
1 | /** 教程页面 |
Service层
1 | package com.dudu.service; |
实现类1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36package com.dudu.service.impl;
/**
* Created by tengj on 2017/4/7.
*/
public class LearnServiceImpl implements LearnService {
LearnMapper learnMapper;
public int add(LearnResouce learnResouce) {
return this.learnMapper.add(learnResouce);
}
public int update(LearnResouce learnResouce) {
return this.learnMapper.update(learnResouce);
}
public int deleteByIds(String[] ids) {
return this.learnMapper.deleteByIds(ids);
}
public LearnResouce queryLearnResouceById(Long id) {
return this.learnMapper.queryLearnResouceById(id);
}
public List<LearnResouce> queryLearnResouceList(Map<String,Object> params) {
PageHelper.startPage(Integer.parseInt(params.get("page").toString()), Integer.parseInt(params.get("rows").toString()));
return this.learnMapper.queryLearnResouceList(params);
}
}
Mybatis集成
接下来,我们分别来介绍下注解方式以及XML配置方式。
方案一:注解方式
Mybatis注解的方式好简单,只要定义一个dao接口,然后sql语句通过注解写在接口方法上。最后给这个接口添加@Mapper注解或者在启动类上添加@MapperScan(“com.dudu.dao”)注解都行。
如下:1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59package com.dudu.dao;
/**
* Created by tengj on 2017/4/22.
* Component注解不添加也没事,只是不加service那边引入LearnMapper会有错误提示,但不影响
*/
public interface LearnMapper {
("insert into learn_resource(author, title,url) values(#{author},#{title},#{url})")
int add(LearnResouce learnResouce);
("update learn_resource set author=#{author},title=#{title},url=#{url} where id = #{id}")
int update(LearnResouce learnResouce);
(type = LearnSqlBuilder.class, method = "deleteByids")
int deleteByIds(@Param("ids") String[] ids);
("select * from learn_resource where id = #{id}")
(id = "learnMap", value = {
(column = "id", property = "id", javaType = Long.class),
(property = "author", column = "author", javaType = String.class),
(property = "title", column = "title", javaType = String.class)
})
LearnResouce queryLearnResouceById(@Param("id") Long id);
(type = LearnSqlBuilder.class, method = "queryLearnResouceByParams")
List<LearnResouce> queryLearnResouceList(Map<String, Object> params);
class LearnSqlBuilder {
public String queryLearnResouceByParams(final Map<String, Object> params) {
StringBuffer sql =new StringBuffer();
sql.append("select * from learn_resource where 1=1");
if(!StringUtil.isNull((String)params.get("author"))){
sql.append(" and author like '%").append((String)params.get("author")).append("%'");
}
if(!StringUtil.isNull((String)params.get("title"))){
sql.append(" and title like '%").append((String)params.get("title")).append("%'");
}
System.out.println("查询sql=="+sql.toString());
return sql.toString();
}
//删除的方法
public String deleteByids(@Param("ids") final String[] ids){
StringBuffer sql =new StringBuffer();
sql.append("DELETE FROM learn_resource WHERE id in(");
for (int i=0;i<ids.length;i++){
if(i==ids.length-1){
sql.append(ids[i]);
}else{
sql.append(ids[i]).append(",");
}
}
sql.append(")");
return sql.toString();
}
}
}
需要注意的是,简单的语句只需要使用@Insert、@Update、@Delete、@Select这4个注解即可,但是有些复杂点需要动态SQL语句,就比如上面方法中根据查询条件是否有值来动态添加sql的,就需要使用@InsertProvider、@UpdateProvider、@DeleteProvider、@SelectProvider等注解。
这些可选的 SQL 注解允许你指定一个类名和一个方法在执行时来返回运行 允许创建动态 的 SQL。 基于执行的映射语句, MyBatis 会实例化这个类,然后执行由 provider 指定的方法. 该方法可以有选择地接受参数对象.(In MyBatis 3.4 or later, it’s allow multiple parameters) 属性: type,method。type 属性是类。method 属性是方法名。 注意: 这节之后是对 类的 讨论,它可以帮助你以干净,容于阅读 的方式来构建动态 SQL。
方案二:XML配置方式
xml配置方式保持映射文件的老传统,优化主要体现在不需要实现dao的是实现层,系统会自动根据方法名在映射文件中找对应的sql,具体操作如下:
编写Dao层的代码
新建LearnMapper接口,无需具体实现类。1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9package com.dudu.dao;
public interface LearnMapper {
int add(LearnResouce learnResouce);
int update(LearnResouce learnResouce);
int deleteByIds(String[] ids);
LearnResouce queryLearnResouceById(Long id);
public List<LearnResouce> queryLearnResouceList(Map<String, Object> params);
}
修改application.properties 配置文件1
2
3
4#指定bean所在包
mybatis.type-aliases-package=com.dudu.domain
#指定映射文件
mybatis.mapperLocations=classpath:mapper/*.xml
添加LearnMapper的映射文件
在src/main/resources目录下新建一个mapper目录,在mapper目录下新建LearnMapper.xml文件。
通过mapper标签中的namespace属性指定对应的dao映射,这里指向LearnMapper。
1 | <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> |
更多mybatis数据访问操作的使用请参考:mybatis官方中文参考文档
分页插件
上面我有使用到物理分页插件pagehelper,用法还算简单,配置如下
pom.xml中添加依赖1
2
3
4
5<dependency>
<groupId>com.github.pagehelper</groupId>
<artifactId>pagehelper-spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
<version>1.1.0</version>
</dependency>
然后你只需在查询list之前使用PageHelper.startPage(int pageNum, int pageSize)方法即可。pageNum是第几页,pageSize是每页多少条。1
2
3
4
5
public List<LearnResouce> queryLearnResouceList(Map<String,Object> params) {
PageHelper.startPage(Integer.parseInt(params.get("page").toString()), Integer.parseInt(params.get("rows").toString()));
return this.learnMapper.queryLearnResouceList(params);
}
分页插件PageHelper项目地址: https://github.com/pagehelper/Mybatis-PageHelper
最终项目效果如下,增删改查分页一个都不少: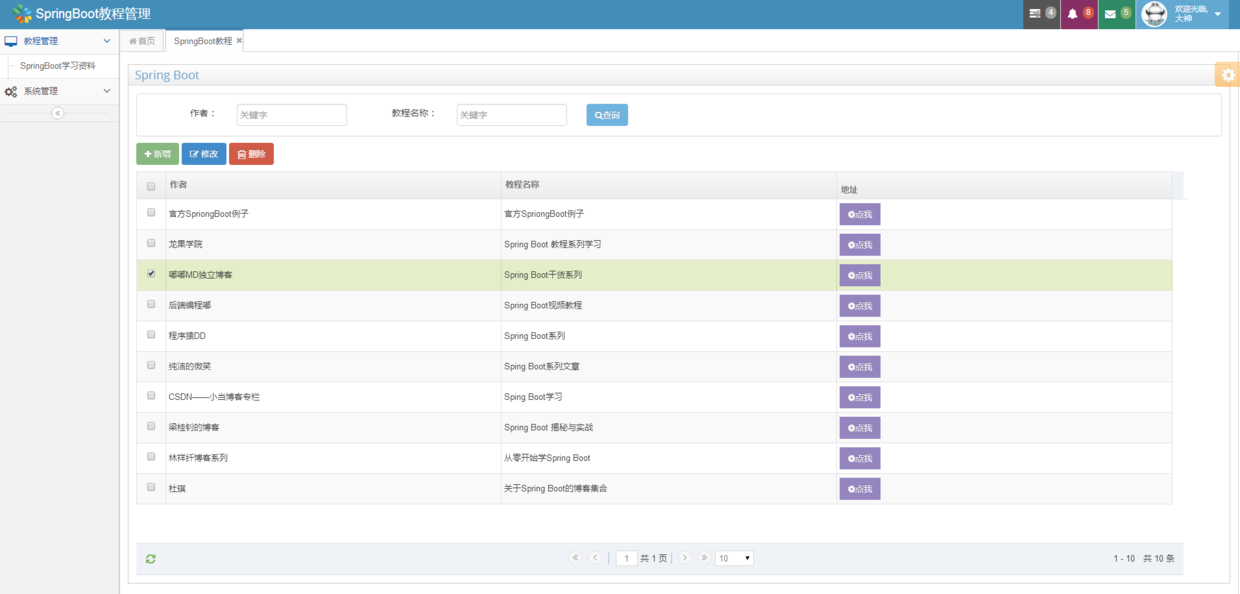
总结
到此为止,Spring Boot与Mybatis的初步整合就完成了,项目不仅整合了bootstrap模板框架,还包含了登录、拦截器、日志框架logback等前面介绍的功能。麻雀虽小,五脏俱全。
想要查看更多Spring Boot干货教程,可前往:Spring Boot干货系列总纲
源码下载
( ̄︶ ̄)↗[相关示例完整代码]
- chapter9==》Spring Boot干货系列:(九)数据存储篇-SQL关系型数据库之MyBatis-注解方式
- chapter9-2==》Spring Boot干货系列:(九)数据存储篇-SQL关系型数据库之MyBatis-XML配置方式
想要ace模板源码的话,在博主公众号回复关键字:ace
一直觉得自己写的不是技术,而是情怀,一篇篇文章是自己这一路走来的痕迹。靠专业技能的成功是最具可复制性的,希望我的这条路能让你少走弯路,希望我能帮你抹去知识的蒙尘,希望我能帮你理清知识的脉络,希望未来技术之巅上有你也有我,希望大爷你看完打赏点零花钱给我。
#
订阅博主微信公众号:嘟爷java超神学堂(java2Learn)三大好处:
- 获取最新博主博客更新信息,首发公众号
- 获取大量视频,电子书,精品破解软件资源
- 可以跟博主聊天,欢迎程序媛妹妹来撩我
